BEM
Motivation
The Boundary Element Method (BEM) plays an important role for the simulation of wave propagation. As it is only necessary to know (or calculate) the sound field on the surface of objects, the BEM is often used for exterior problems in unbounded domains. At the ARI the BEM is implemented in AcouBEM using the so called collocation approach with constant elements, and the implementation is used in several projects ranging from the calculation of HRTFs to the simulation of the effectiveness of noise barriers. For that reason the BEM implementation is constantly adapted to new problems and continously updated with new routines. The code for 3D problems is also used for Mesh2HRTF.
Die Burton Miller Methode
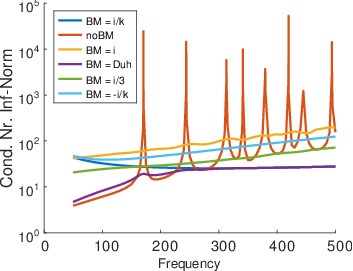
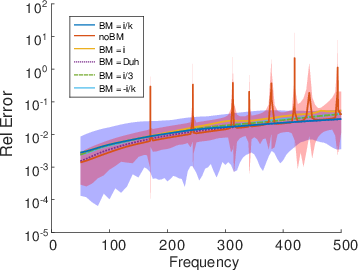
In AcouBEM the Burton-Miller method is used to guarantee a stable and unique solution of a scattering problem for all frequencies. In a nutshell the Burton-Miller method is based on the combination of two different representations of the Helmholtz equations. In this combination the so called Burton-Miller factor plays an important role and especially in the low frequency regions one can find a lot of different methods and suggestions on how to set this parameter.
Using the example of a sound hard sphere, one can see that the choice of the BM factor plays an important role for the stability of the system which can be represented by the condition number. A large number has negativ effect on the accuracy of the calculated solution.
Adaptivity
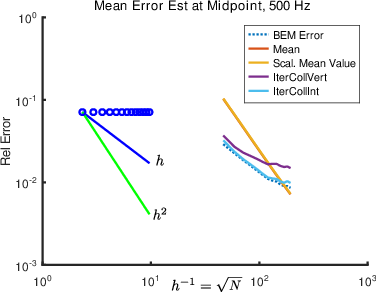
The accuracy of the BEM solution is mainly dependent on the size of the used elements and the frequency. As a rule of thumb it is suggested to use at least six to eight elements per wavelength. Adaptivity now means that the program automatically detects at which part ot the scatterers surface the solution is not accurate enough, and thus, where the accuracy of the calculations needs to be enhanced for example by subdiving one or more elements. To that end, it is essential to have a good and reliable "local" error estimator, that is close to the actual error. At the ARI different methods for such an estimator are investigated.