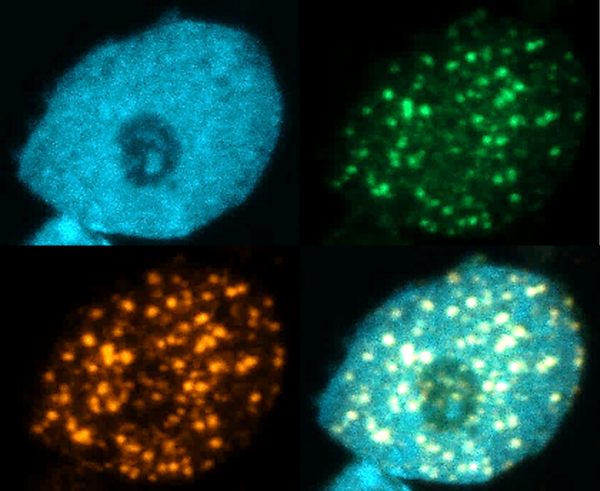
DNA damage response protects genome integrity by quickly repairing DNA lesions. Most plant proteins involved in this process have…
Frédéric Berger
Evolution of Chromatin

Research Focus
In eukaryotes, DNA is wrapped around nucleosomes. Nucleosomes consist of proteins called histones and help organize DNA into functional units, they are thus critical for all cellular processes that affect DNA. Nucleosome properties are modulated by their composition in different variants of histone proteins. In addition, chemical modifications of histones regulate nucleosome properties. These modifications are deposited, erased and bound by different protein complexes that form chromatin. Chromatin is the recipient of the epigenetic code that influences how the transcription and DNA repair machineries operate. Because chromatin is present is all eukaryotes, it must have evolved both in prokaryotes and during eukaryogenesis.
The Berger lab investigates the evolution of chromatin and its impacts on processes such as transcription, DNA repair and meiosis. Genetics, genomics, and biochemical analyses are combined with synthetic strategies to study chromatin in models of Archaeplastida, yeast, E. coli and Asgard Archeae.