Hydrogen cluster-jet target
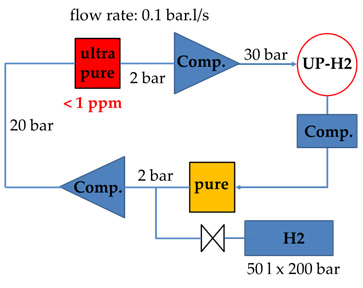
Within the EU framework programme HadronPhysics, our Institute contributes to studies of the (hydrogen) cluster-jet target of PANDA. A continuous working of the cluster-jet beam, without blocking due to freezing of impurities in the nozzle, is essential for the use in PANDA. Therefore, a gas purification system in the sub-ppm region is a must. SMI is performing R&D work to develop a system which has to work at high gas throughput and at high pressure to achieve the required cluster-jet density for PANDA. In addition, first studies have been started for the design of a closed-cycle deuterium gas system.
LH2 Target for CERN
It is proposed to study polarization effects in the production of antiprotons at the PS test beam line T11 with a momentum of 3.5 GeV/c. A polarization in the production process has never been studied, but if existing, it would allow for a rather simple and cheap way to generate a polarized antiproton beam with the existing facilities at CERN.

The production of antiprotons is typically done by bombarding a solid target with high momentum protons. At CERN the beam momentum is about 24 GeV/c and the number of collected antiprotons is in the order of one per 106 beam protons.
In order to measure the polarization of the produced antiprotons a further scattering of antiprotons is necessary in a process with known and sufficient analysing power. Therefor as scattering target, a liquid hydrogen cell with a length of 15 cm has been constructed.

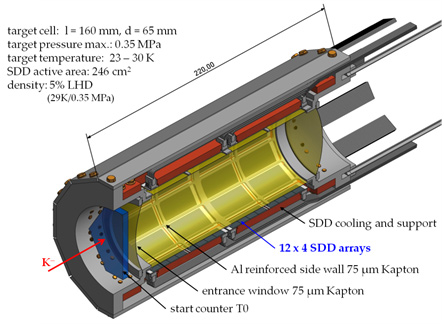
Cryogenic hydrogen gas targets for K-d
The importance of kaonic deuterium X-ray spectroscopy has been well recognized, for more than 30 years (Richard Dalitz), but no experimental results have yet been obtained due to the difficulty of the X-ray measurement. Therefore we are preparing two slightly different setups to perform a K-d experiment either at DAFNE at LNF, Frascati, Italy or at J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex), Tokai, Japan.
Because of the different antikaon production method, the cryogenic target cells have to be optimised for each machine, although the newly developed SDDs will be used in both cases.